About
What are CCAs?
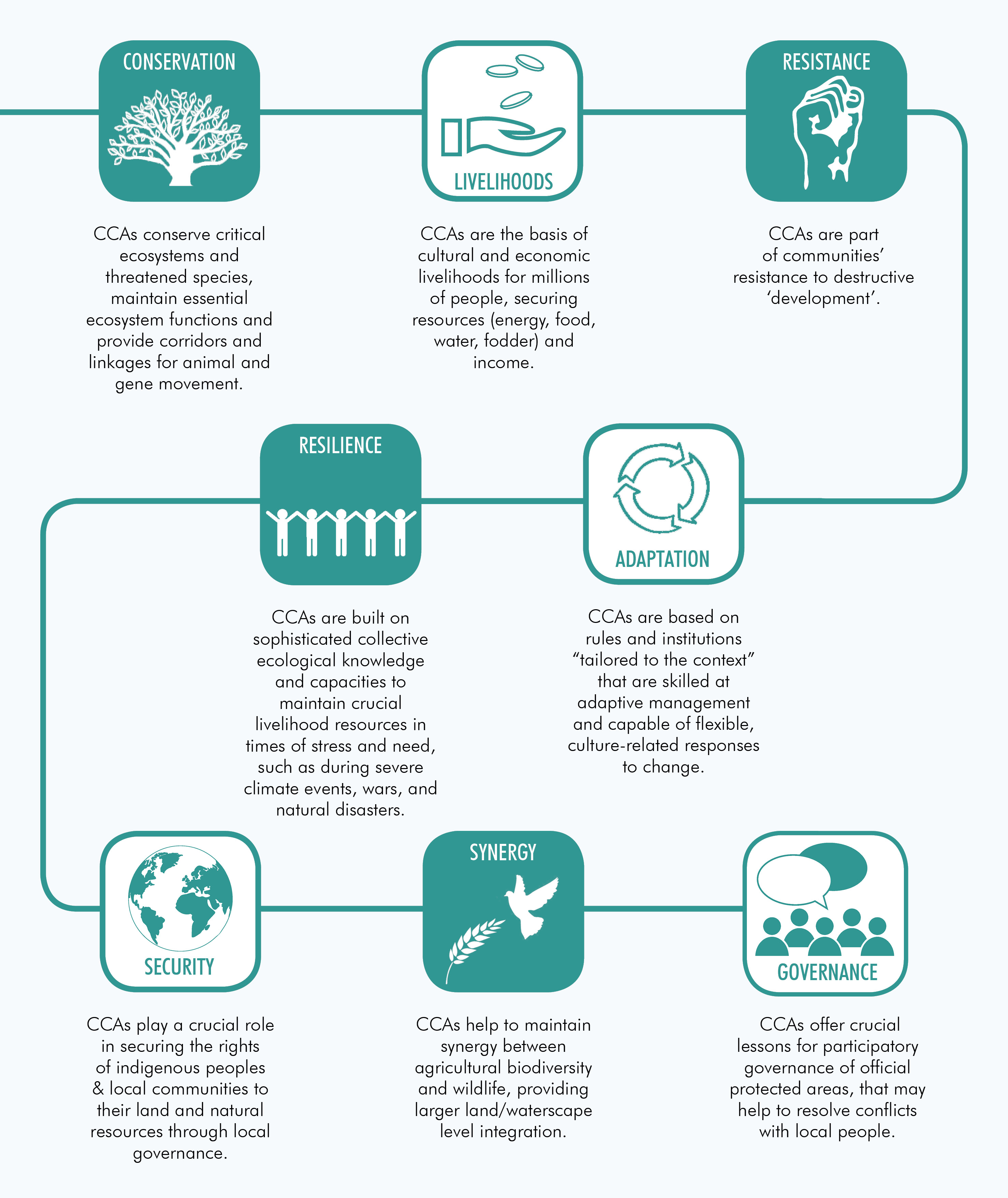
There are several examples across South Asia where deep connections exist between an area and the local community, usually rooted in history, socio-cultural identity, spirituality and/or people’s reliance on the area for their livelihood and wellbeing. Community based conservation practices also exist in non-traditional and urban areas. In India, such areas are referred to as Community Conserved Areas (CCAs). Internationally, they are referred to as “Territories and Areas Conserved by Indigenous Peoples and Local Communities (ICCAs)” or “territories of life”. The three definitive characteristics of a CCA are:
- · The community is the main decision maker for the area (even if not legally)
- · The community makes and enforces rules and regulations for conservation
- · The efforts contribute to the conservation of nature
This portal also includes areas which do not fulfil the above three criteria but desire to do so, or ones where conservation efforts have been disrupted due to poor practices, relocation or restrictive legal policies. CCAs on this portal are thus marked Defined, Desired, Disrupted or Data Deficient.
CCAs are not recognised legally in many South Asian countries. However, they are well recognised and supported by global networks and alliances.
Why This Portal
South Asia has a rich history of community-based conservation. These conservation efforts include diverse customary, institutional and collective practices. It is estimated that traditional territories cover 22% of world’s land surface and hold 80 percent of the planet’s biodiversity.
The conventional approach to biodiversity conservation is to demarcate land and declare it a “Protected Area”. Based on the colonial concept of protecting nature from people, this approach does not recognise customary sustainable use as a form of conservation. Many South Asian countries have a colonial history and follow this approach to conservation. In India there are over 800 protected areas, almost 5% of the country’s geographical area, in Nepal there are over 30 covering over 33% area, in Bangladesh there are over 30 covering 1% area and in Pakistan, there are over 200 covering 10% of its area.
However, it is now becoming evident that this approach is largely failing, causing immense danger to the long term security of many wild fauna and flora and livelihood and cultural security of millions of human communities dependent on these areas.
Research shows that in the last two decades while the global coverage of protected areas has increased in both numbers and spread, biodiversity has declined at population, species, ecosystem and possibly genetic levels. Currently, one million species are threatened with extinction - more than ever before in human history.
Lack of people’s participation in management and governance of protected areas and lack of recognition of Indigenous Peoples’ and Local Communities’ own conservation practices have been identified as some of the reasons for this decline of biological diversity.
Within discourses and practice, though some changes have occurred in legal policies relevant to CCAs, CCAs have remained largely invisible and unrecognised.
The mission of this portal is in the above context.
Our Mission
Our mission is to enhance the understanding of and strengthen the narrative about the role played by Community Conserved Areas in conservation of biological diversity and community wellbeing in larger landscapes in South Asia.
Our Methodology
This portal is an open source platform where communities and community based organisations across South Asia can view and provide data.
The core team invites local communities and partner organisations to contribute to this growing database of knowledge on the multi-dimensional values of CCAs and their vital contributions to the conservation of biodiversity. The data contributed on this site is under Creative Commons License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0). Anyone can upload data. The data is not verified by the core team.
Any registered user can provide data through a short, multiple choice questionnaire for each CCA. The questions regarding the location of the CCA, its ecosystem, the people involved, its legal status, land ownership and more. If you wish to provide more detailed information regarding a CCA, please write to [email protected].
Data on this portal is sourced in multiple ways: information available in the public domain, information provided by a community member or gathered through participation of the entire community or information provided by an external entity.